|

| 摘要:
In this paper, we propose an energy management strategy based on deep reinforcement learning for a hybrid battery system in electric vehicles consisting of a high-energy and a high-power battery pack. The energy management strategy of the hybrid battery system was developed based on the electrical and thermal characterization of the battery cells, aiming at minimizing the energy loss and increasing both the electrical and thermal safety level of the whole system. Primarily, we designed a novel reward term to explore the optimal operating range of the high-power pack without imposing a rigid constraint of state of charge. Furthermore, various load profiles were randomly combined to train the deep Q-learning model, which avoided the overfitting problem. The training and validation results showed both the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed strategy in loss reduction and safety enhancement. The proposed energy management strategy has demonstrated its superiority over the reinforcement learning-based methods in both computation time and energy loss reduction of the hybrid battery system, highlighting the use of such an approach in future energy management systems. |
部分图片:
| | 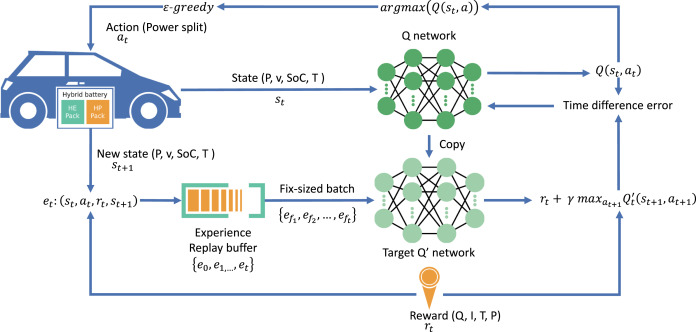
图1 The framework of the DQL-based EMS for the HBS in BEVs. | 引文信息:
W. Li, H. Cui, T. Nemeth, J. Jansen, C. ünlübayir, Z. Wei, L. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. Ruan, H. Dai, X. Wei, D.U. Sauer, Deep reinforcement learning-based energy management of hybrid battery systems in electric vehicles, Journal of Energy Storage. 36 (2021) 102355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.102355.(下载链接)
| 其他相关论文: Xiong R., Cao J., Yu Q., Reinforcement learning-based real-time power management for hybrid energy storage system in the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. Appl. Energy, 211 (2018), pp. 538-548, 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.11.072.(下载链接) |
|